0. Overview
In XPath Part 1, we covered the essential concepts and basic syntax of XPath necessary for web crawling. In Part 2, we will delve into advanced topics of XPath.
1. Understanding Wildcards
Before diving into advanced topics, it is essential to understand the meaning of the '*' (wildcard) in XPath.
- The wildcard '*' in XPath matches any element and is used to select all elements. Let's explain with an example.
//div[contains(@class, "aa")]
The above XPath represents a div element with a class name containing 'aa'. What if we use a wildcard instead of div?
//*[contains(@class, "aa")]
In the above XPath, '*' matches all elements, so the XPath selects all elements with a class name containing 'aa'.
2. Understanding XPath Hierarchy
Now let's move on to the advanced topics of XPath.
Here is a simple HTML code snippet.
<AAA>
<BBB>
<CCC/>
<DDD/>
</BBB>
<EEE>
<FFF>
<GGG/>
<GGG/>
<III>
<JJJ/>
</III>
</FFF>
</EEE>
<KKK>
<LLL/>
</KKK>
</AAA>
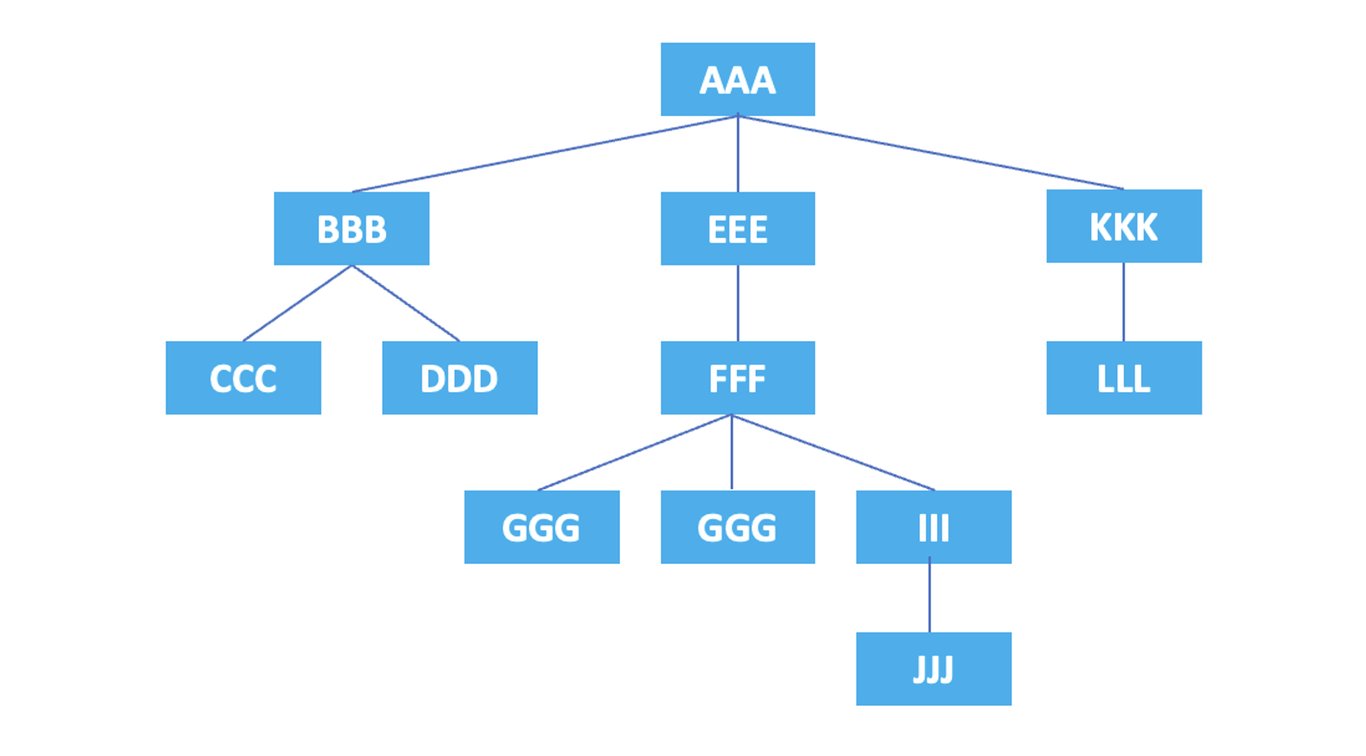
Each element and attribute in HTML forms a hierarchical relationship, and XPath represents this hierarchy in a tree structure. Axes in XPath indicate the direction or relationship used to reference and select nodes (data points, units) in the tree structure. Axes include self axis, parent axis, child axis, etc. Let's explain each using examples below.
If we represent the hierarchical structure of the elements in a diagram, it looks like this:
Now, let's see how nodes can be represented using axes.
3. Representation of Nodes
3.1. self
: Represents the current node itself.
/AAA/self::*
The XPath above selects the current node, the <AAA> element.
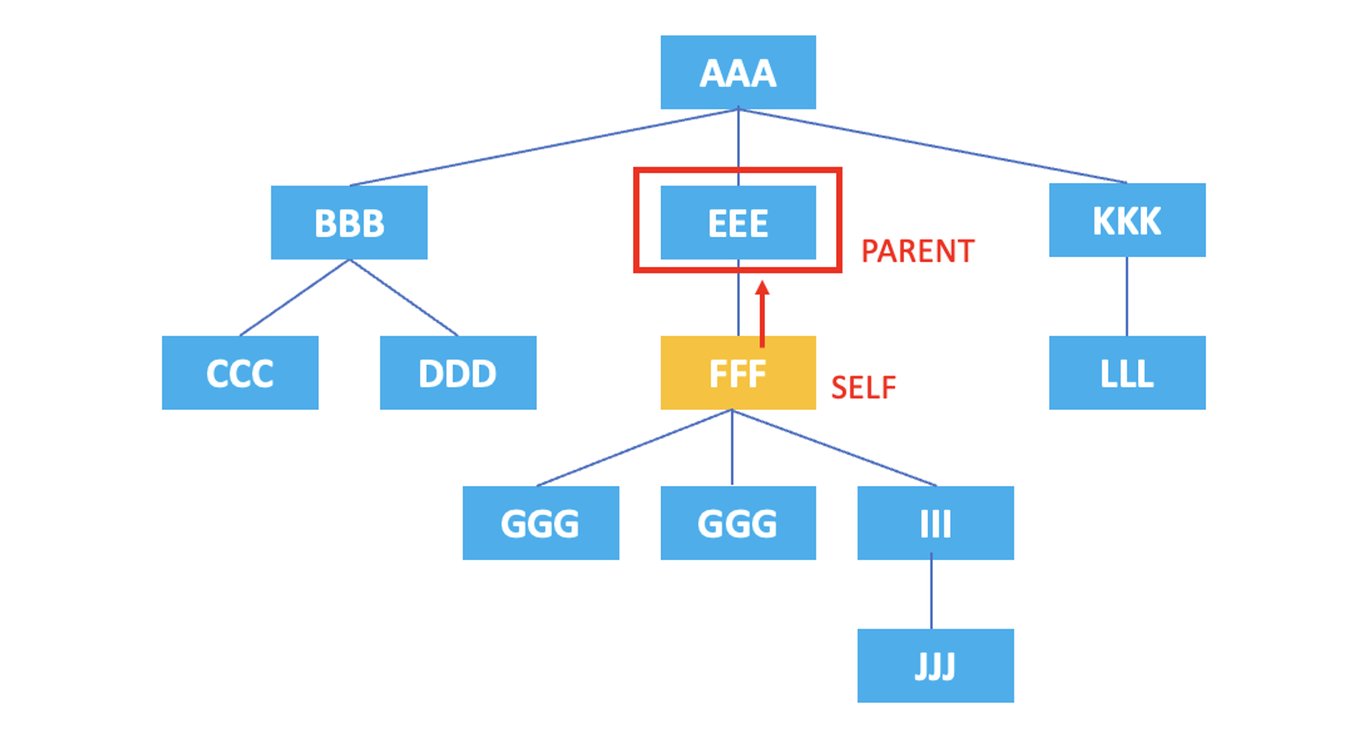
3.2. parent
: Represents the parent node of the current node.
/AAA/EEE/FFF/parent::*
The XPath above selects the parent node of the current node, the <EEE> element, which is the parent of the <FFF> element.
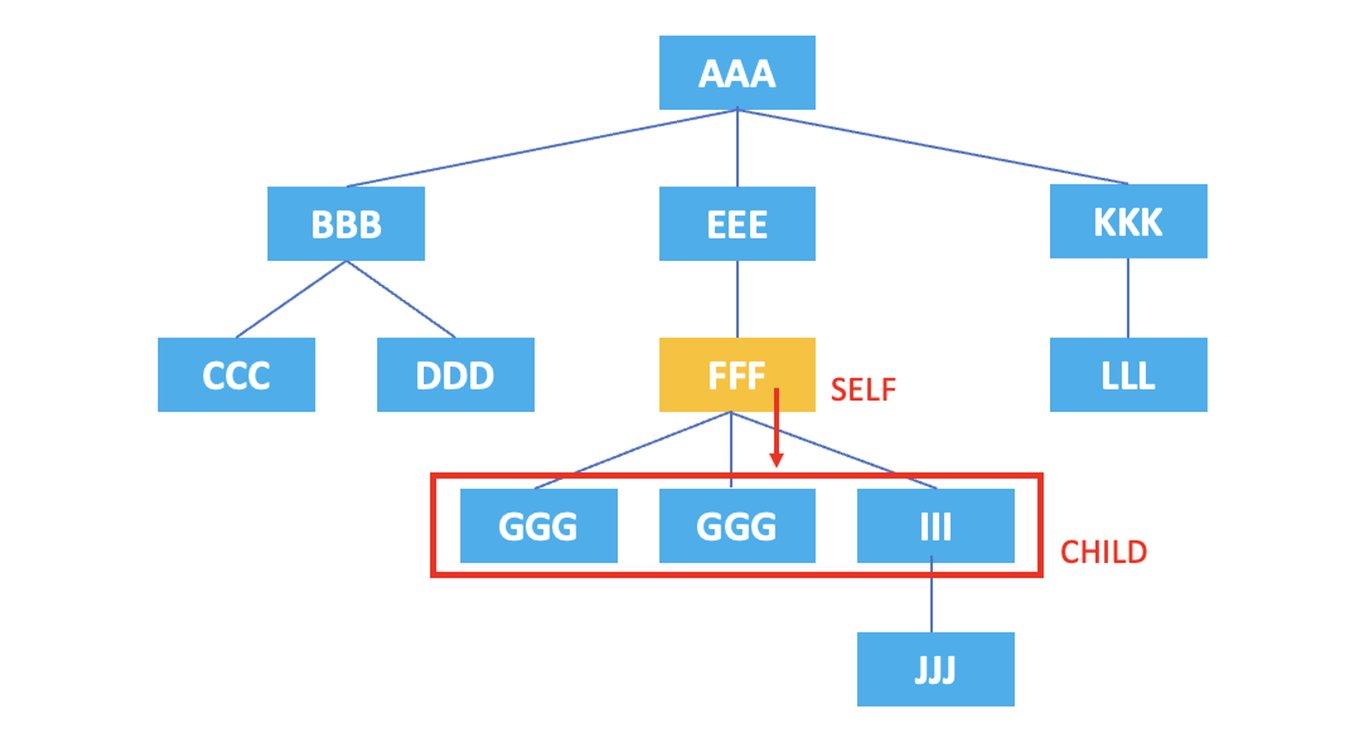
3.3. child
: Represents the child nodes of the current node.
/AAA/EEE/FFF/child::*
The XPath above selects all child nodes of the current node, the <FFF> element, which are <GGG>, <HHH>, <III>.
If you only want to select the <III> element, you can modify the XPath as follows.
/AAA/EEE/FFF/child::III
Also, if you want to select the first <GGG> element among the two, you can modify it as follows.
/AAA/EEE/FFF/child::GGG[1]
Note that unlike most other programming languages, XPath indexes start from 1!
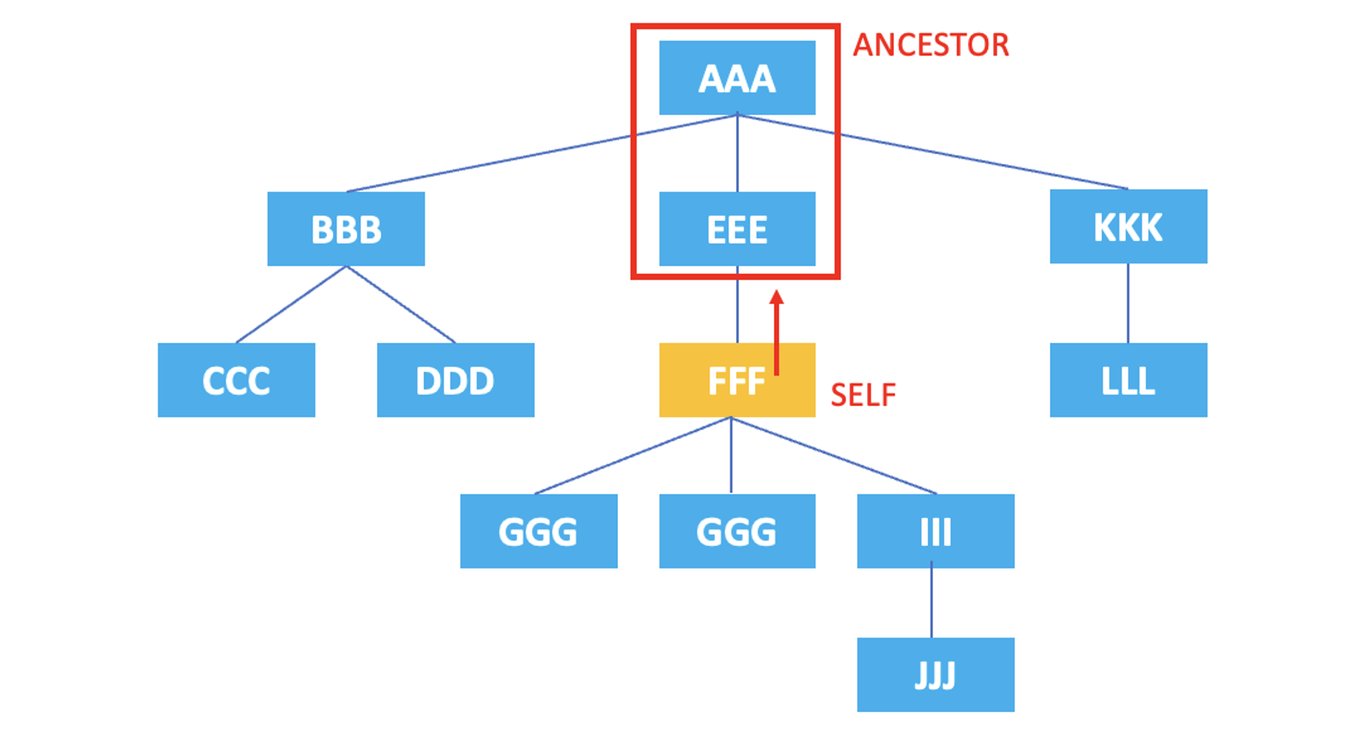
3.3. ancestor
: Represents all ancestor nodes of the current node.
/AAA/EEE/FFF/ancestor::*
The XPath above selects all ancestor nodes of the current node, the <FFF> element, which are <EEE> and <AAA>.
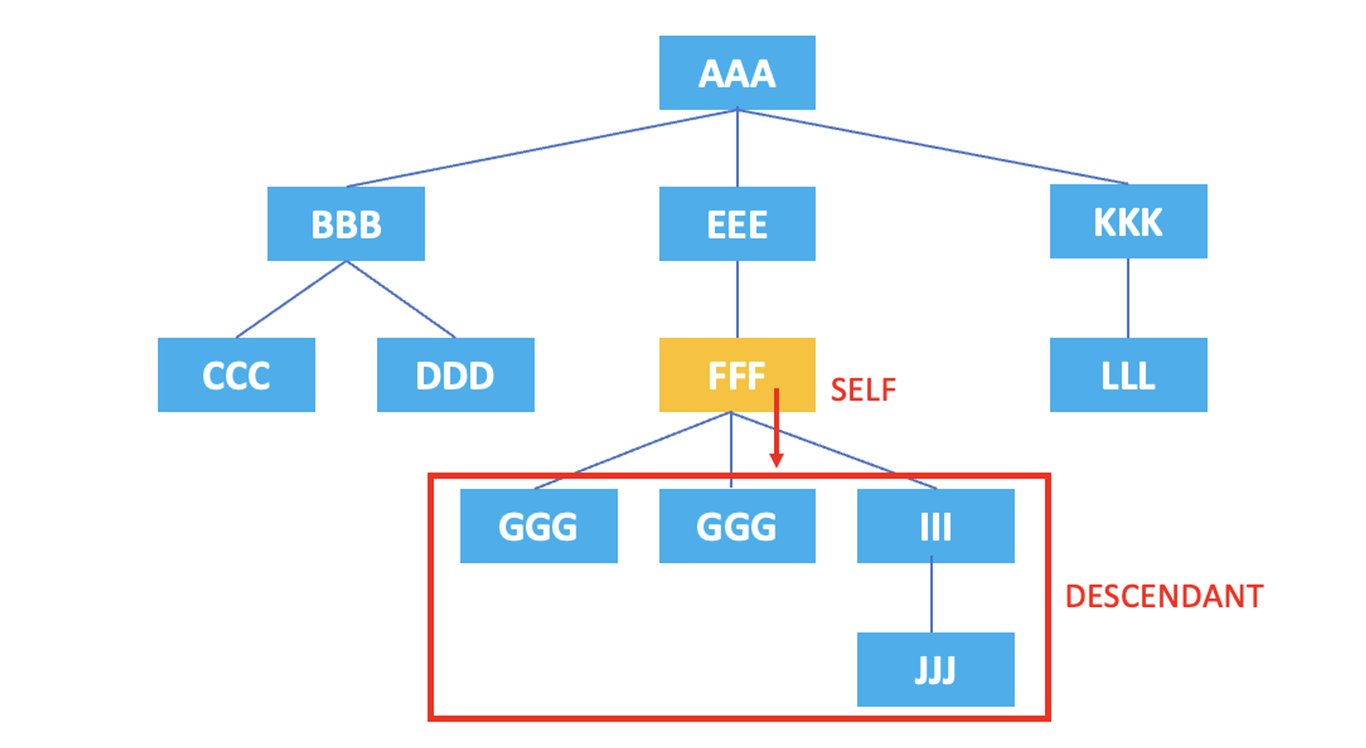
3.4. descendant
: Represents all descendant nodes of the current node.
/AAA/EEE/FFF/descendant::*
The XPath above selects all descendant nodes of the current node, the <FFF> element, which are <GGG>, <HHH>, <III>, <JJJ>.
3.5. ancestor-or-self
: Represents the current node and all ancestor nodes of the current node.
/AAA/EEE/FFF/ancestor-or-self::*
The XPath above selects both the current node, <FFF>, and all ancestor nodes, <EEE> and <AAA>.
3.6. descendant-or-self
: Represents the current node and all descendant nodes of the current node.
/AAA/EEE/FFF/descendant-or-self::*
The XPath above selects both the current node, <FFF>, and all descendant nodes, <GGG>, <HHH>, <III>, <JJJ>.
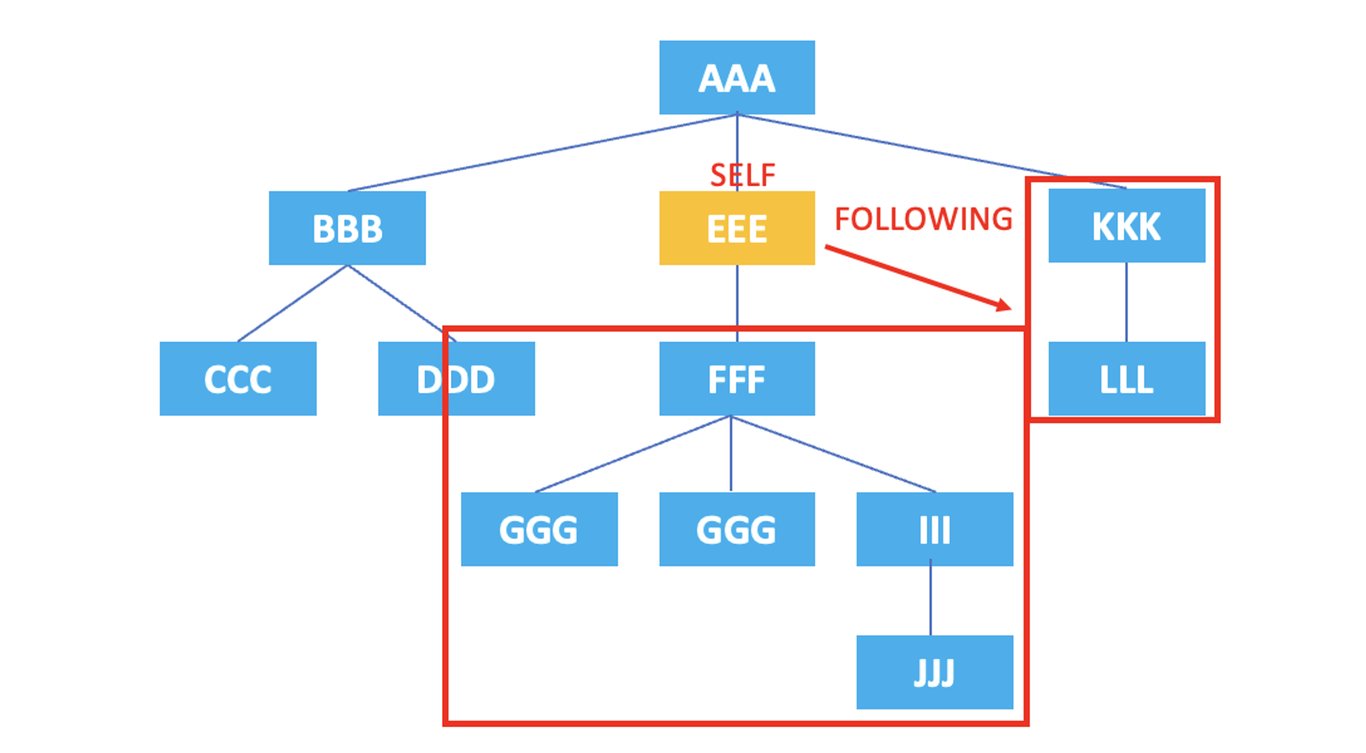
3.7. following
: Represents all nodes that come after the current node's tag.
/AAA/EEE/following::*
The XPath above selects all nodes that come after the current node, <EEE>, which are <FFF>, <GGG>, <HHH>, <III>, <JJJ>, <KKK>, <LLL>.
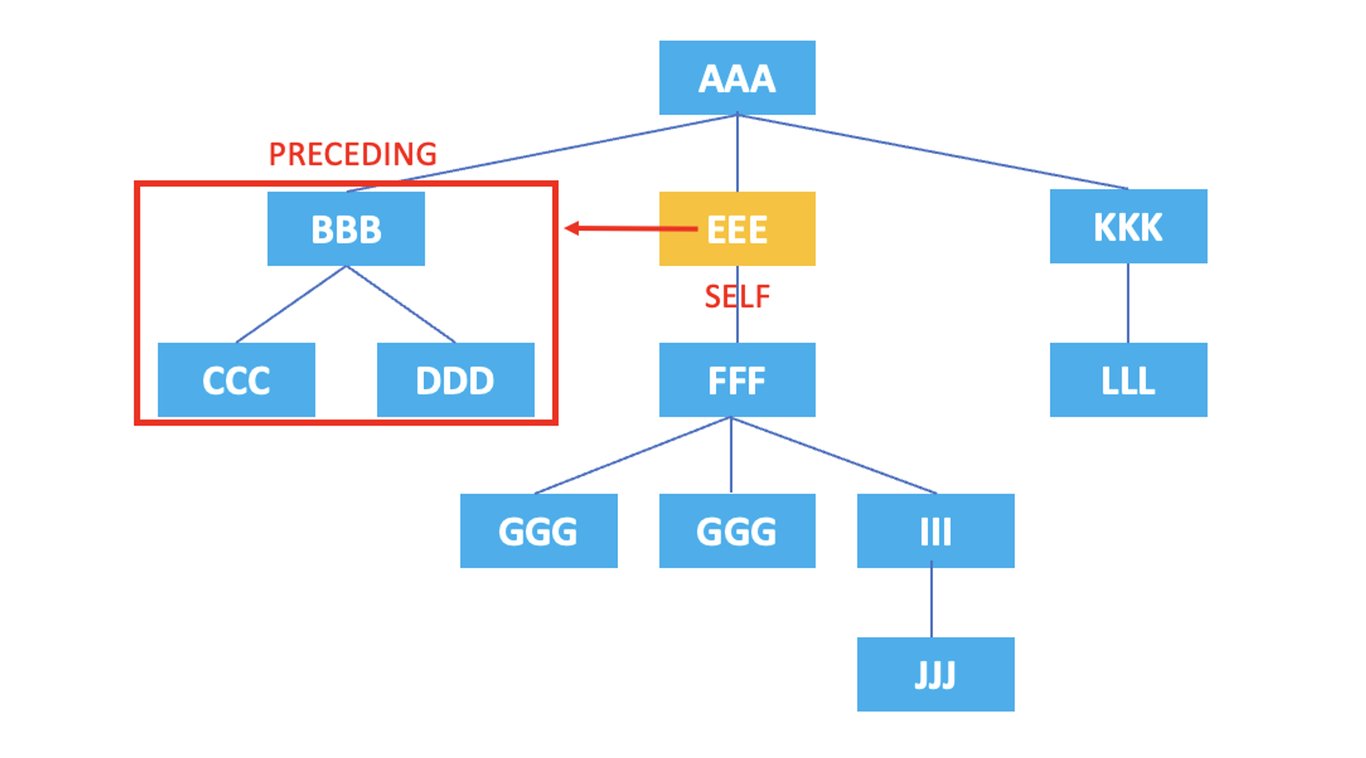
3.8. preceding
: Represents all nodes that come before the current node's tag starts.
/AAA/EEE/preceding::*
The XPath above selects all nodes that come before the current node, <EEE>, which are <BBB>, <CCC>, <DDD>.
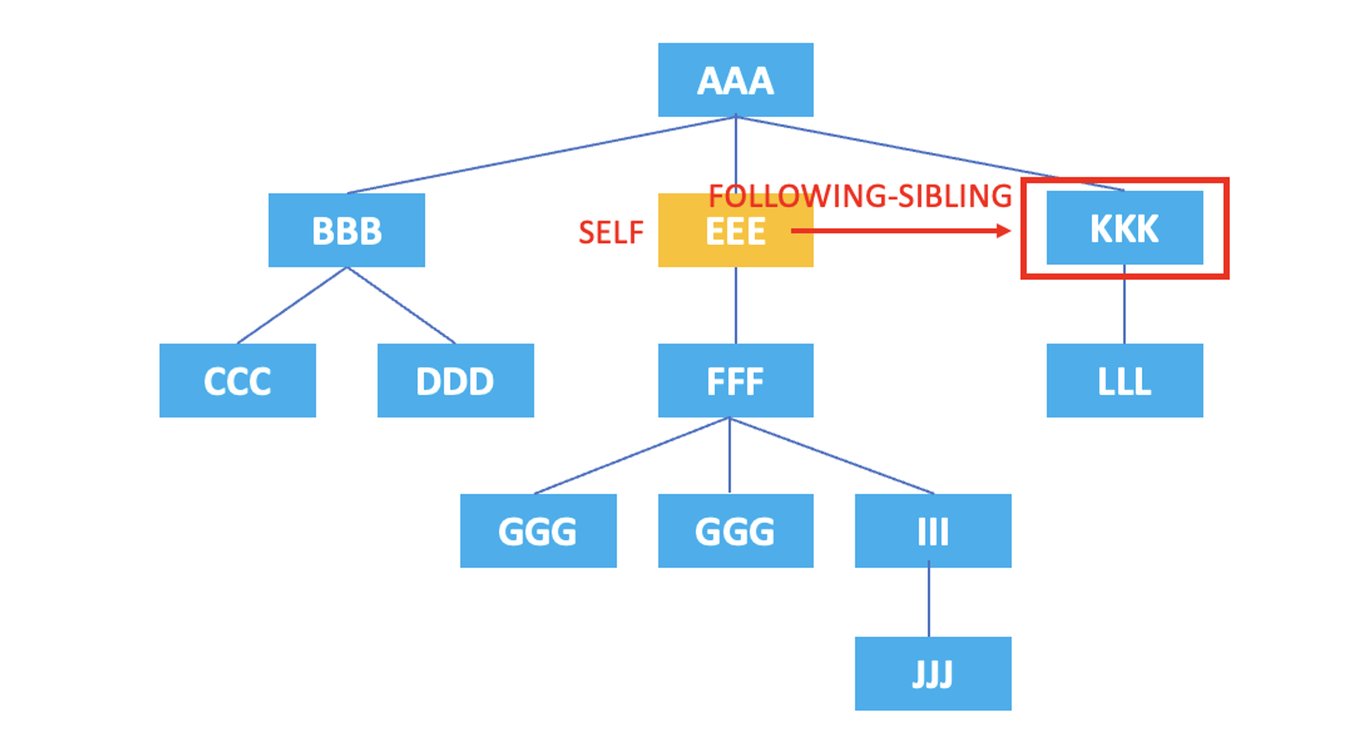
3.9. following-sibling
: Represents all sibling nodes that come after the current node.
/AAA/EEE/following-sibling::*
The XPath above selects the sibling node, <KKK>, that comes after the current node, <EEE>.
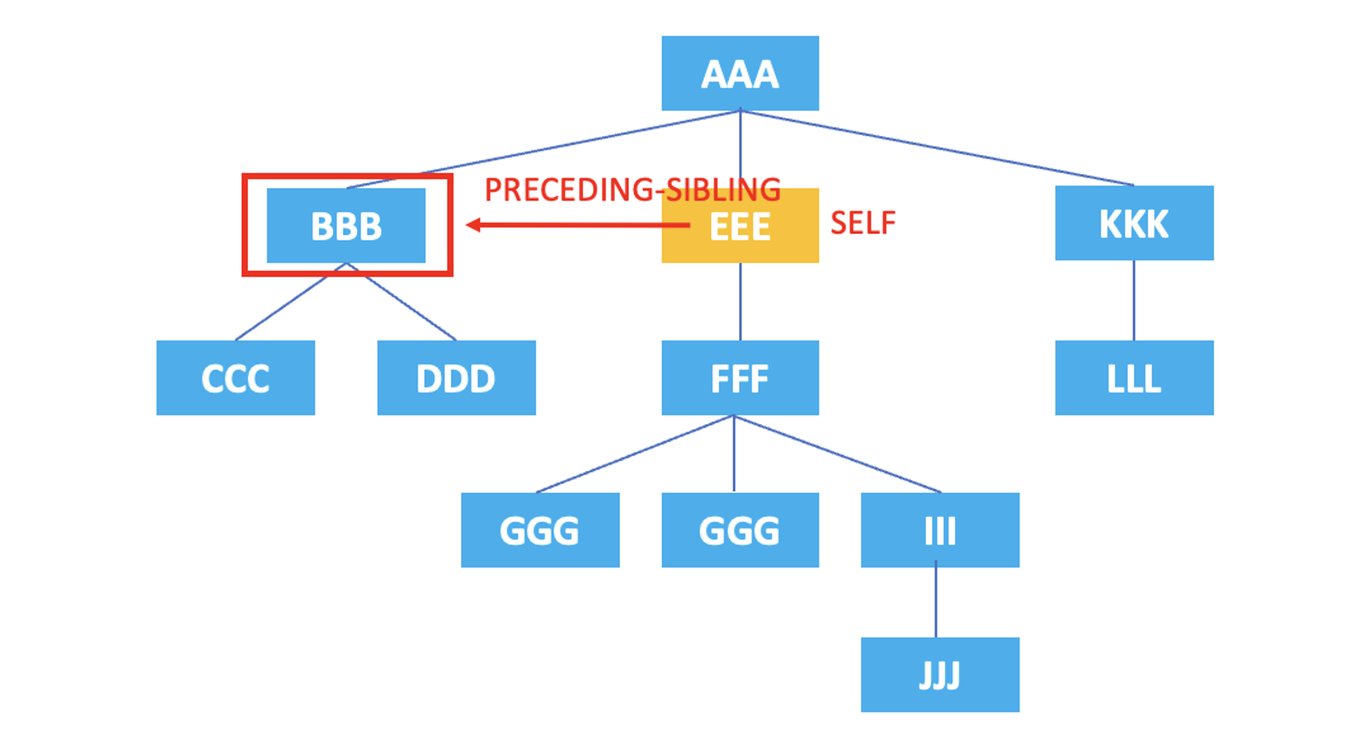
3.10. preceding-sibling
: Represents all sibling nodes that come before the current node.
/AAA/EEE/preceding-sibling::*
The XPath above selects the sibling node, <BBB>, that comes before the current node, <EEE>.
So far, we have looked at the axes used to represent nodes in XPath.
Additionally, let's explore two other functions that can be used in XPath.
4. Functions Used in XPath
4.1. count
: Returns the number of nodes that meet specific conditions.
#class 속성 값이 ‘example인 div 요소의 개수를 반환
count(//div[@class="example"])
#p 요소의 총 개수를 반환
count(//p)
4.2. position
: Returns the position of the current node. (The position starts from 1 and increases sequentially.)
<root>
<item>Item 1</item>
<item>Item 2</item>
<item>Item 3</item>
</root>
For example, when you have the following XML code, you can write XPath as follows.
//item[position() = 2]
Using the position function, you can select the second item element among three item elements.
5. Conclusion
We have now covered advanced topics in XPath. If you have mastered XPath from basics to advanced, you should have acquired the foundational knowledge necessary to accurately locate and extract data from XML documents using XPath.
XPath is a powerful tool for navigating and manipulating XML documents, widely used in practical applications such as data scraping, web crawling, and extracting data from XML-based web services. We hope you succeed in efficiently extracting and utilizing data using XPath!
Also, check out this article:
Data Collection, Automate Now
Start crawling 5,000+ websites in 5 minutes without coding experience