0. Introduction
I have prepared a post for developers who are interested in digital image processing or need to process images in actual projects.
Removing backgrounds or extracting main colors from photos is utilized in various fields such as digital art, web development, mobile apps, and machine learning projects.
Although it may seem like complex algorithms or high-level skills are required to perform these tasks, it is actually very easy.
By utilizing Python libraries like FastAPI, rembg, and extcolors, you can easily create these tasks as APIs to be used in various applications. In this post, I will guide you step by step on how to combine these three tools to build a powerful image processing API.
1. Setting Up the Basic Structure of FastAPI
1.1. Installing Required Packages
Install fastapi and uvicorn to run it.
pip install fastapi
pip install uvicorn
1.2. Printing Hello World
Write the following code in main.py:
# 패키지 import
from fastapi import FastAPI
import uvicorn
# Helper 함수 작성
# app = FastAPI()
# Endpoint 함수 작성
# # 루트 페이지("/") 접속 시 "Hello": "world" return
@app.get("/")
def read_root():
return {
"Hello": "world"
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run(app, host='0.0.0.0', port=5000)
We will set the host to '0.0.0.0' and the port to 5000.
1.3. Running the uvicorn Server
Enter the following in the terminal:
uvicorn main:app --reload
INFO: Will watch for changes in these directories: ['PROJECT_DIRECTORY_PATH']
INFO: Uvicorn running on <http://127.0.0.1:8000> (Press CTRL+C to quit)
INFO: Started reloader process [9982] using StatReload
The uvicorn server is running at http://127.0.0.1:8000!
You can confirm that the return value is displayed correctly when accessing the root page.
2. Creating a Background Removal and Color Extraction API
2.1. Installing Required Packages
Install the necessary packages to create the API:
pip install image
pip install rembg
pip install extcolors
Import as follows:
import os
import request
from PIL import Image
from extcolors import extract_from_image
from rembg import remove
2.2. Image Saving Helper Function
Let's first create a helper function that takes an image URL and saves the image file.
In HTML's <img> tag, there is an src attribute, and this function accesses that attribute to retrieve the image file.
def save_image(image_url):
response = requests.get(image_url)
# 이미지 저장 디렉토리
download_dir_name = 'downloaded_images'
if response.status_code == 200:
# 파일 이름 얻기
image_name = os.path.basename(image_url)
# 파일 이름에 확장자 없다면 추가
exts = [".jpg", ".jpeg", ".png", ".gif"]
ext_included = False
file_ext = None
for ext in exts:
if ext in image_name:
ext_included = True
file_ext = ext
break
if ext_included:
image_name = image_name.split(file_ext)[0] + file_ext
else:
image_name += ".jpeg"
file_ext = ".jpeg"
# 저장 경로 없다면 생성
if not os.path.exists(download_dir_name):
os.makedirs(download_dir_name)
# 파일 경로 얻기
image_path = os.path.join(download_dir_name, image_name)
# 파일 저장
with open(image_path, 'wb') as f:
f.write(response.content)
result = {
"message": "Image saved successfully!",
"status_code": response.status_code,
"image_path": image_path,
"image_name": image_name,
"file_ext": file_ext
}
return result
else:
return {
"message": "Failed to save image",
"status_code": response.status_code
}
2.3. Helper Function to Convert RGB to HEX
There are various ways to display colors, but in this API, we extract colors and provide RGB and HEX information.
Let's create a helper function that extracts colors from the image, converts them to RGB, and then to HEX.
def rgb_to_hex(rgb_tuple):
r = int(rgb_tuple[0])
g = int(rgb_tuple[1])
b = int(rgb_tuple[2])
return '#' + hex(r)[2:].zfill(2) + hex(g)[2:].zfill(2) + hex(b)[2:].zfill(2)
2.4. Background Removal Endpoint Function
http://127.0.0.1:8000/rembg/{IMAGE_URL}
When you access the above URL, an endpoint function will be created to save the image, remove the background, and return the image path and name.
@app.get('/rembg/{url:path}')
def remove_image_background(url: str):
image_info = save_image(url) # 이미지 저장
image_path = image_info["image_path"]
image_name = image_info["image_name"]
file_ext = image_info["file_ext"]
image_name_without_ext = image_name.rsplit(file_ext, 1)[0]
image = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGBA')
output = remove(image)
convert_dir_name = 'converted_images'
# 저장 경로 없다면 생성
if not os.path.exists(convert_dir_name):
os.makedirs(convert_dir_name)
out_image_path = os.path.join(convert_dir_name, f'{image_name_without_ext}_rembg.png')
output.save(out_image_path, 'PNG')
result = {
"message": "The background of the image is successfully removed",
"image_path": out_image_path,
"image_name": image_name
}
return result
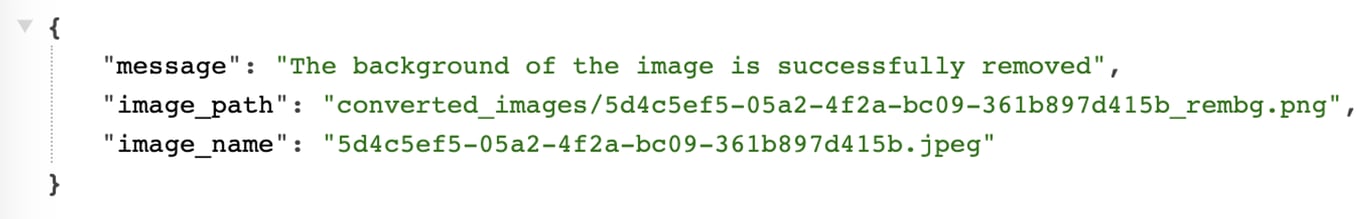
Execution Result:
I have executed it with the following image URL:
I successfully received the path and name of the image with the background removed.
...
(remaining content has been truncated)