Sentiment analysis is one of the important fields of natural language processing that automatically analyzes the emotions or opinions of text data. Over the past few years, a deep learning model called BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) has shown high performance in natural language processing tasks and has played a significant role in sentiment analysis. In this blog, we will explore how to perform sentiment analysis using BERT.
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Sentiment Analysis
Natural language processing is a field that enables machines to understand and process human language, including understanding and processing text data.
Sentiment analysis is a significant subfield of natural language processing, which involves determining whether a given text has positive, negative, or neutral sentiments.
Sentiment analysis is utilized in various fields, such as managing product reputation in business, adjusting strategies by understanding customer opinions, predicting market sentiments in the financial sector for investment decisions, and analyzing feedback in customer service to improve service quality.
2. What is BERT?
BERT is a language model based on the Transformer architecture developed by Google, which can understand words and contexts within sentences and effectively process text data. BERT is a pretrained model that has been successfully applied to various natural language processing tasks after being trained on large-scale text data. Let's take a look at the code for performing simple text sentiment analysis using BERT.
3. Sentiment Analysis with BERT
3.1. Installing Libraries
First, install the Transformers library using the pip command.
!pip install transformers
Next, import the necessary libraries.
import torch
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertForSequenceClassification
import torch.nn.functional as F
The "kykim/bert-kor-base" model we will use is a Korean BERT model trained in Korean for Korean natural language processing research. 'BertForSequenceClassification' is a model class for fine-tuning the BERT model for text sequence classification tasks.
3.2. Specifying the Tokenizer
Next, specify the tokenizer. Most transformer models do not directly take text as input but require tokenized input. By using the BertTokenizer.from_pretrained function, you can automatically get the required tokenizer for each model.
model_name = "kykim/bert-kor-base"
model = BertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_name, num_labels=2)
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
3.3. Performing Classification (Sentiment) with a Function
Define the 'classify_emotion' function to perform sentiment analysis on input text. Tokenize the input text using the specified tokenizer, make predictions using the model, convert the prediction results into probabilities using the softmax function, and select the class (emotion) with the highest probability among the returned probabilities using the argmax function for output.
def classify_emotion(text):
# 텍스트 토큰화 및 패딩
tokens = tokenizer(text, padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
# 예측 수행
with torch.no_grad():
prediction = model(**tokens)
# 예측 결과를 바탕으로 감정 출력
prediction = F.softmax(prediction.logits, dim=1)
output = prediction.argmax(dim=1).item()
labels = ["부정적", "긍정적"]
print(f'[{labels[output]}]\n')
3.4. Displaying Sentiment Analysis Results
Finally, input a sentence from the user through the 'predict_sentence' function, call the 'classify_emotion' function to perform sentiment analysis, and display the results.
def predict_sentence():
input_sentence = input('문장을 입력해 주세요: ')
classify_emotion(input_sentence)
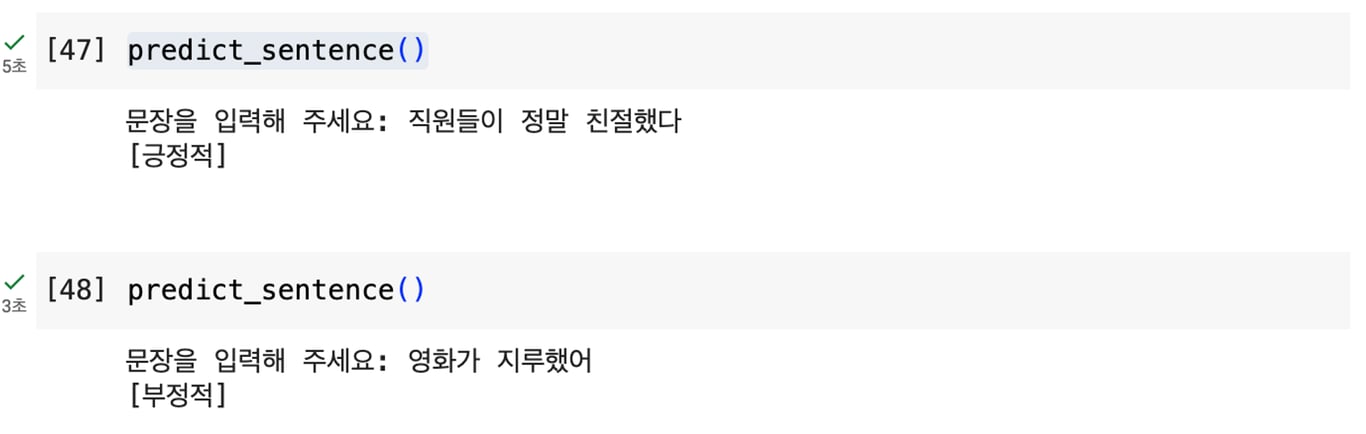
predict_sentence()
By running the above code, you can perform sentiment analysis as shown in the image.
4. Conclusion
By using the basic BERT model for sentiment analysis, you can quickly and easily obtain results. However, this model has limitations in terms of accuracy.
To overcome these limitations, you can use Fine-Tuning to fine-tune the base model for specific tasks. Fine-Tuning is a process of adjusting the weights of the model to make it more suitable for a specific domain or task and improve accuracy.
For example, training the BERT model on sentiment-related datasets can yield more accurate results for sentiment analysis.
Therefore, if you seek higher accuracy, it is recommended to apply Fine-Tuning.
Also, check out this article:
Data Collection, Automate Now
Start in 5 minutes without coding · Experience with 5,000+ website crawls